Michigan Med-aphor
Problem
UM surgical residents require real-time feedback during Fundamentals of Laparoscopic Surgery training at the simulation center to enhance their performance in laparoscopic surgery.
Our Goal
Develop an intuitive and immersive system for surgical residents to receive feedback during FLS training when attending physicians are unavailable.
Our Response
Develop a gamified training system that provides real-time and post-practice feedback to surgical residents without requiring the presence of attending physicians.
Project Details
Working Team: UX & Interaction Design Team (University of Michigan)
Stakeholders: Surgical Residents, Clinical Educators, Attending Physicians
Timeline: 3 months (academic project)
Scope:
User Research, Workflow Mapping, Interaction Design, Prototyping, Usability Testing
My Role: User Experience Researcher & Designer
User Research
Methods: Contextual Interviews, Empathy Interviews, Behavioral Observation, Thematic Analysis, Affinity Mapping
Tools: Zoom, Miro
Workflow & Journey Analysis
Methods: User Journey Mapping, Task Analysis, Pain Point Identification, Scenario Mapping
Tools: Miro, Whiteboarding
Interaction & UX Design
Methods: Sketching, Wireframing, Interaction Modeling, Low- to Mid-Fidelity Prototyping
Tools: Paper Prototypes, Figma
Testing & Iteration
Methods: Usability Testing, Feedback Synthesis, Iterative Refinement
Tools: Zoom, Miro
Proxy Users
Surgical residents from China were interviewed as proxy users due to the
unavailability of real users.
2. Lack of Peer Support
Users did not have any peer support and would usually train alone.
3. Signs of boredom
Users required an interactive system that would relieve them from boredom.
4. Contextual Inquiry
Contextual inquiry through in-person observation of user environments.
Key Project Highlights
5. User Feedback
Feedback from proxy users, peers, experts and stakeholders
6. User Mental Model
Solutions based on user’s mental models, motivation and system integration.
Design Process
-

User Interviews
Through user interviews, we gained a deeper understanding of the context in which our system is used, as well as user actions, pain points, and suggestions for improving the system.
-

Personas
By creating personas based on user research, we were able to develop reliable representations of common user needs and behaviors.
-
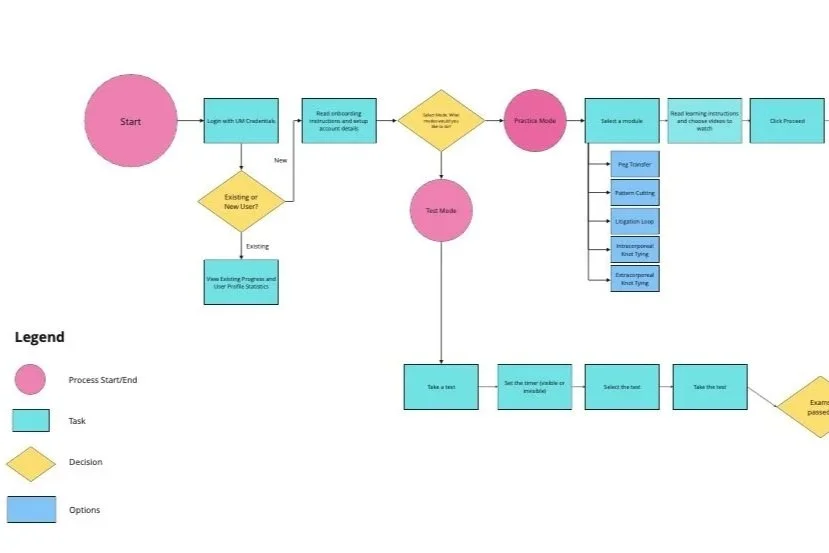
User Journey Map
Using a User Journey Map, we were able to visualize and analyze the actions and interactions of our users on multiple levels. This allowed us to prioritize crucial user actions and improve the overall flow of the user experience.
-

Narrative Storyboard
By creating storyboards, we gained a better understanding of how users navigate through our system, and how their needs interact with the system's functionalities. The visual narrative of the storyboards allowed us to identify the sequential steps that users take to perform actions, and to improve the flow of the system accordingly.
-

Usability Testing
By conducting usability testing with both proxy users and peers, we were able to identify usability and design issues, and iterate on our product based on user feedback. Through this process, we gained a better understanding of their observations and actions.
-
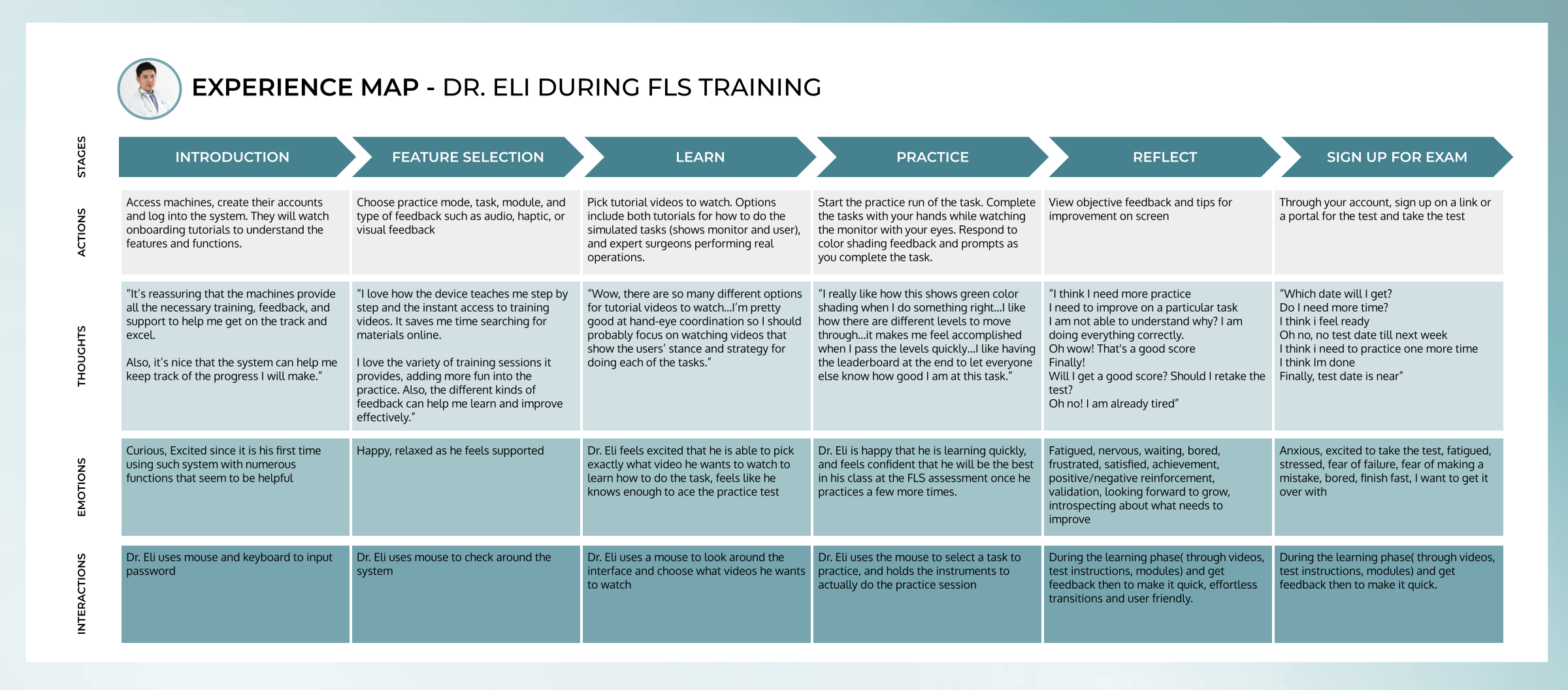
User Experience Map
The User experience map enabled us to get a comprehensive understanding of user’s experience, with regards to user’s actions, user’s interactions, user’s emotions and user’s thoughts. It enabled the team to collaboratively understand and arrive at decisions that enhanced user experiences and system interactions.
Users can choose between the following feedback and training modes:
Visual: Color and Text Commentary
Audio: Spoken prompts
Tactile: Haptic Feedback via Vibrations
Modes: Test Practice, Simulated Surgery, Games
Miscellaneous: Timer, Grading, etc.
Solution
A system providing real-time and post-practice feedback via a gamified training experience, accessible without an attending.
Key system features:
Onboarding experience for training
Step-by-step instructions for tasks and educational videos
Various activities and scenarios to choose from to modify training experience
Real-time and post-practice feedback, including qualitative and quantitative
Comparative benchmarking and contact support with peers
User customization of real-time and post-practice feedback settings, that adapt the simulated learning experience.
Gamification of training to provide a multi-modal delivery of feedback and visual guidance.
Key Takeaways
-
Designer Bias
To prioritize user needs and pain points, it's crucial to challenge designer assumptions and identify and address any designer bias.
-
Real users vs Proxy users
Usability testing should involve diverse users, but if real users aren't available, creative proxy user testing can still provide valuable feedback for improving design.
-
User safety and Risk management
Anticipating and mitigating potential issues can be facilitated by considering risk management and failure analysis before and during the design process.


